

The source is described by a general "source strength" S because there are many ways to characterize a radiation source - by grams of a radioactive isotope, source strength in Curies, etc. All measures of exposure will drop off by inversesquare law. to test the gravitational Inverse Square Law at: (1) submillimeter scale and (2) at. HyperPhysics***** Electricity and MagnetismĪs one of the fields which obey the general inverse square law, a point radiation source can be characterized by the relationship belowwhether you are talking about Roentgens, rads, or rems. ONERA The French Aerospace Lab, 29 avenue de la Division Leclerc.

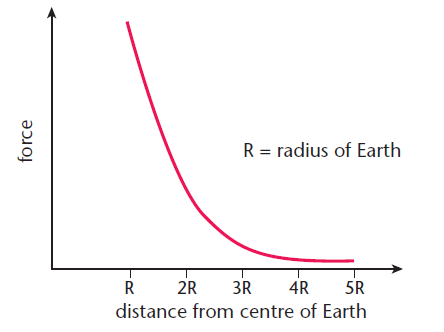
Other applications of the inverse square law Coulomb was actually doing his experiments about 10 years. The electric force in Coulomb's law follows the inverse square law. Henry Cavendishs experiment to measure the value of G, the universal gravitational constant. Other applications of the inverse square lawĪs one of the fields which obey the general inverse square law, the electric field of a point charge can be put in the form shown below where point charge Q is the source of the field. It is a subject of continuing debate with a source such as a skunk on top of a flag pole will its smell drop off according to the inverse square law?Īpplications of the inverse square law: GravityĪs one of the fields which obey the general inverse square law, the gravity field can be put in the form shown below, showing that the acceleration of gravity, g, is an expression of the intensity of the gravity field. Brightness of light and loudness of sound. 4 times weaker (according to inverse square law) zero. Point sources of gravitational force, electric field, light, sound or radiation obey the inverse square law. Terms in this set (27) The force of gravity between two objects gets weaker with the square of the distance. Being strictly geometric in its origin, the inverse square law applies to diverse phenomena. The intensity of the influence at any given radius r is the source strength divided by the area of the sphere. This comes from strictly geometrical considerations. The signal is detected by a supercon-ducting differential accelerometer, making a highly sensitive sensor of the gravity force generated by the source mass.Inverse Square Law Inverse Square Law, GeneralĪny point source which spreads its influence equally in all directions without a limit to its range will obey the inverse square law. Two test masses, also disk-shaped, are suspended on the two sides of the source mass at a distance of 100 μm to 1 mm. Inverse square law states that the intensity of the radiation is inversely proportional to the square of the distance. To minimize Newtonian errors, ISLES employs a near-null source of gravity, a circular disk of large diameter-to-thickness ratio. The low-damping magnetic levitation, combined with a low-noise SQUID, leads to extremely low intrinsic noise in the detector. Point-like sources of gravitational forces, electric fields, light, sound and radiation. As designed, the experiment will be cooled to less than 2 K in NASA’s low temperature facility the LTMPF, allowing superconducting magnetic levitation in microgravity to obtain very soft, low-loss suspension of the test masses. Many concepts in the physics curricula can be explained by the inverse square law. The measures to be applied for reducing the effects of disturbances will be described in this presentation.

To accomplish these goals on the rather noisy International Space Station, the experiment is set up to provide immunity from the vibrations and other common-mode accelerations. ISLES will be sensitive enough to detect axions with the strongest allowed coupling and to test the string-theory prediction with R⩾5 μ m.
The objective of ISLES (inverse-square law experiment in space) is to perform a null test of Newton’s law on the ISS with a resolution of one part in 10 5 at ranges from 100 μm to 1 mm.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
